CBGA, also known as cannabigerolic acid, is the precursor to all other cannabinoids in cannabis and hemp plants. For this reason, people often refer to CBGA as the ‘mother cannabinoid.’
Without CBGA, no other cannabinoids, including CBD and THC, would exist. However, it is also possible that it has some health benefits of its own. Here is all you need to know about the CBGA cannabinoid.
What Is CBGA?
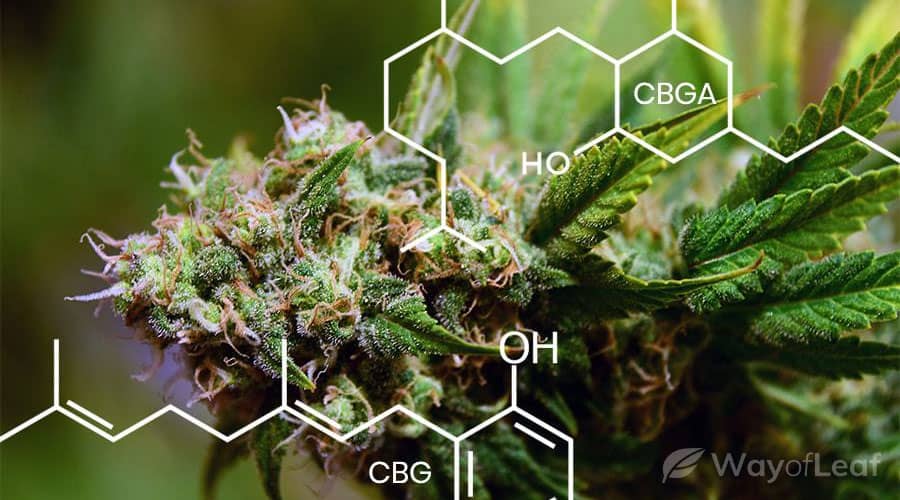
CBGA is a cannabinoid, one of the myriad active compounds that cannabis and hemp plants produce. It is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, which derives from a chemical known as an olivetolic acid. We will discuss the exact process by which CBGA forms later in the article.
The CBGA structure is similar to that of other cannabinoids in that it contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Its exact molecular formula is C₂₂H₃₂O₄. The compound consists of a ring of carbon atoms. This ring is attached to two long carbon chains, two oxygen atoms, and a carboxyl group (COOH). It is the carboxyl group that makes the compound mildly acidic.
One unique feature of CBGA is that it is the precursor to all other cannabinoids. These cannabinoids include the well-known duo CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol). CBGA also forms the less common cannabinoids CBN (cannabinol), CBC (cannabichromene), and CBG (cannabigerol), among others.
CBG and CBGA have many similarities, as CBGA is the acidic form of CBG. However, their chemical structure is slightly different since CBG does not include a carboxyl group. The molecular formula of CBG is C₂₁H₃₂O₂.
CBGA Benefits
The world is beginning to recognize that cannabinoids like CBD and THC have many benefits for human health. Although we know less about CBGA, it may have some valuable properties of its own.
However, before we delve into the potential health benefits of CBGA, there are a few things to consider.
Firstly, the current research on CBGA is quite limited. Scientists have completed most of their studies in laboratories using cell samples or animal models. Therefore, the exact effects of CBGA on the human body remain unknown.
Secondly, these studies used lab-grade CBGA, which is different from the CBGA that naturally occurs in cannabis. Although the chemical itself is the same, the quantities that the plant produces are relatively low.
Finally, much of the current research focuses on CBG rather than CBGA. We have included studies on both cannabinoids as their effects are likely to be similar. So, what does the research say?
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
A 2013 study investigated the effects of CBG on a mouse model of colitis (inflammation of the bowel). The results showed that the cannabinoid reduced inflammation and the formation of free radicals in the intestine. It also reduced nitric oxide production, a chemical that experts believe plays a role in the development of the disease.
These results tie in with those of another 2018 study, which confirmed CBG’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. The authors suggest that the compound could act as a neuroprotectant, defending nerve cells from harmful oxidative stress.
Potential Benefits for Diabetes
Another possible benefit of CBGA involves diabetes. A 2018 study found that CBG and CBGA and CBD and CBDA reduce the activity of aldose reductase. Aldose reductase is an enzyme that is associated with many diabetic complications.
Furthermore, a 2019 study found that CBGA, CBDA, and CBG could help with the metabolism of lipids (fats). This finding could potentially benefit patients with metabolic disorders like diabetes and dyslipidemia in the future.
Of course, research into CBGA is only just beginning. More studies are necessary to confirm how this cannabinoid could benefit the human body. Watch this space to learn more about the latest cannabinoid research as it emerges.
Does CBGA Become CBDA?
Experts consider CBGA to be the precursor of all other cannabinoids. This means it is responsible for forming CBD and CBDA, which are well-known for their health benefits. For this reason, some people believe that CBGA is the most important cannabinoid of all.
The process of transforming CBGA into CBDA relies on an enzyme called cannabidiolic acid synthase (CBDAS). When this enzyme becomes available, it can convert CBGA into CBDA. You may not have heard of CBDA, but it is the acidic form of CBD.
Cannabis and hemp plants produce all of their cannabinoids in acid form. With the help of time and heat, these acids undergo decarboxylation, which converts them to their more active counterparts.
Decarboxylation is a critical process. Not only does it convert CBDA into CBD, but it also turns THCA into THC. Without decarboxylation, the compounds in cannabis and hemp have far fewer effects.
CBGA Biosynthesis: Explaining the Process
The biosynthesis of cannabigerolic acid is a complex process. It occurs in the resinous trichomes of the cannabis plant. Trichomes are tiny glands that coat the plant’s buds and leaves, producing most of its active compounds. It is possible to see them with the naked eye, and they look like little crystals coating the outside of the plant. Under the microscope, trichomes look like tiny mushrooms with a stalk and a bulbous head.
The primary purpose of trichomes is to produce cannabinoids and other compounds like terpenes. These chemicals help to protect the plant from predators like herbivores. They also offer some defense against mold and other microbes.
In the trichomes, CBGA starts as a short-chain fatty acid called hexanoic acid. An enzymatic reaction then converts it to olivetolic acid. This chemical then reacts with a compound called geranyl diphosphate, and the enzyme CBGA synthase (CBGAS) converts it into CBGA.
Further enzymatic reactions change CBGA into the acidic forms of the other cannabinoids. For example, CBDA synthase converts CBGA into CBDA, and THCA synthase converts CBGA into THCA. Meanwhile, decarboxylation transforms cannabigerolic acid into cannabigerol.
Bottom Line on CBGA
CBGA, or cannabigerolic acid, has received far less press than CBD or THC. However, this compound is an essential component of the cannabis plant as it is responsible for forming all other cannabinoids.
In addition to being the precursor to the other cannabinoids, CBG and CBGA appear to have their own benefits. Studies have shown that these natural compounds have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. They may also play a role in the treatment of diabetes and metabolic disorders.
Although we are just beginning to understand all of these cannabis compounds indications, it is an area of great scientific interest. More and more researchers are now dedicating themselves to studying cannabinoids, and we are likely to learn much more about them in the future.

![What Is Humulene? [Cannabis Terpenes Explained]](https://wayofleaf.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/mj_what_is_humulene_1920-min-640x225.jpg)
![What Is CBL? [Cannabicyclol Explained]](https://wayofleaf.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/mj_what_is_cbl_1920-min-640x225.jpg)



![Does Cannabis Affect Women Differently to Men? [ANSWERED]](https://wayofleaf.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/mj_does-marijuana-affect-women-differently-to-men-answered-640x225.jpg)

![Why CBD Oil Won’t Work for Everyone [Answered]](https://wayofleaf.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/wol_1920x450-67-640x225.jpg)


![What Is Geraniol? [Cannabis Terpene Guide]](https://wayofleaf.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/wol_what-is-geraniol-640x225.jpg)
